what temperature is cold
Server Error Please try later. Hot & Cold: Extreme Temperature Safety Overview If you are planning to travel outdoors, be prepared to deal with all kinds of weather. This could mean extremely rainy days or extremely dry days, and from the hottest hours of the day to the coldest nights. The human body has a normal basic temperature between 97 °F and 99 °F, but on average, a normal body temperature is 98.6 °F (37 °C). To maintain this temperature without the help of heating or cooling devices, the surrounding environment should be about 82 ̊F (28 ̊C). Clothes are not just for the look — they are necessary to keep the heat. It can usually accumulate more layers for colder months, and can use air fans or conditioners in warmer months to maintain a healthy core temperature. In some cases, it can be found in an environment with extreme temperatures. It is crucial to know what health concerns they face, as well as how to avoid any temperature-related health problems. First, take into account that temperature reading in a thermometer is not necessarily the temperature that should be concerned. Relative humidity in your environment can affect the temperature you really feel, which is called the "apparent temperature". Some example scenarios include: High environmental temperatures can be dangerous for your body. In the range of 90° and 105°F (32° and 40°C), you can experience heat cramps and exhaustion. Between 105° and 130°F (40° and 54°C), heat exhaustion is more likely. You must limit your activities in this range. An ambient temperature of more than 130 °F (54 °C) often leads to heat. Other heat-related diseases include:SymptomsThe symptoms of heat-related disease depend on the type and severity of the disease. Some common symptoms of heat exhaustion include: The symptoms of heat storm include: Treatment If someone loses consciousness and shows one or more of the symptoms of heat exhaustion or heat spill, call 911 immediately. To treat heat exhaustion, try to stay cool with cold, wet fabrics around your body and slowly take small sips of water until symptoms begin to fade. Try to get out of the heat. Find a place with air conditioning or a lower temperature (especially outside direct sunlight). Rest on a sofa or bed. To treat heatstroke, cover with cold, wet fabrics or take a cold bath to normalize body temperature. Salt from heat immediately to a place with a lower temperature. Do not drink anything until you (or the person who experiences heat) receive medical care. Prevention Stay well hydrated to better prevent heat-related diseases. Drink enough fluids to make your urine clear or clear. Do not rely only on thirst as a guide to how much fluid you should be drinking. When you lose many fluids or sweat profusely, make sure to replace electrolytes as well. Use appropriate clothing for your environment. Clothes that are too thick or too warm can quickly cause you to get overheat. If you feel too hot, loosen your clothes or remove excess clothes until you feel cool enough. Use sunscreen when possible to prevent sunburn, which makes your body harder to get rid of excess heat. Try to avoid places that can get extremely hot, like cars inside. Never leave another person, child or pet, even for short periods of time. Risk Factors Common risk factors that may cause you to be more susceptible to heat-related disease include: As with high temperatures, it does not depend solely on the thermometer reading of the ambient air to measure cold temperatures. The speed of the wind and humidity of the external body can cause a chill that dramatically changes the cooling rate of your body and how it feels. In extremely cold weather, especially with a high wind cold factor, you can quickly experience the start of hypothermia. Drying in cold water can also result in immersion hypothermia. Some cold-related diseases include: In addition to these diseases, winter time can cause major inconveniences for travelers. Always ready to deal with heavy snow and extreme cold, either on the road or at home. SymptomsWhen your body falls below 98.6 °F (37 °C), you may experience: When your body temperature is between 91.4 ̊ and 85.2 ̊F (33 ̊ and 30 ̊C), you:between 85.2 ̊ ̊F and 71.6 ̊F (30 ̊C and 22 ̊C), you will experience: A body temperature below 71.6 ̊F (22 ̊C) may be extremely severed. Treatment If someone passes, shows several symptoms mentioned above, and has a body temperature of 95°F (35 °C) or lower, call 911 immediately. Make CPR if the person is not breathing or has no pulse. To treat hypothermia, get out of the cold as soon as possible and a warmer atmosphere. Remove any wet or wet clothes and start warming up the mid areas of your body, including your head, neck and chest, with a heating pad or against someone's skin with a normal body temperature. Drink something warm to gradually increase body temperature, but it has nothing alcoholic. Even after you start feeling hot again, stay dry and stay wrapped in a hot blanket. Look for medical help immediately to minimize damage to your body. To treat hestbite, soak the affected area in warm water not hotter than 105 ̊F (40 ̊C) and wrap it in gauze. Keep your toes or fingers affected by the separated frostbite to avoid rubbing the areas together. Do not rub, use, or walk on frozen skin, as this can cause tissue damage. Talk to your doctor if you still can't feel anything on your skin frozen after 30 minutes. Prevention It is essential to protect anyone who experiences early hypothermia symptoms. If possible, remove them from the cold immediately. Do not try to heat a person suffering from severe hypothermia with vigorous exercise or rubbing, as this may lead to other problems. To prevent cold-related diseases, take one or more of these measures when the temperature starts to drop: Risk factors Common risk factors for hypothermia and hestbit include: Last medical review on January 10, 2017Read this below

The Temperature in English - ESL Vocabulary

Temperature – the hot and the cold — Science Learning Hub

The Refrigerator Temperature Your Fridge Should Be Set to (Chart and Tips) | Real Simple
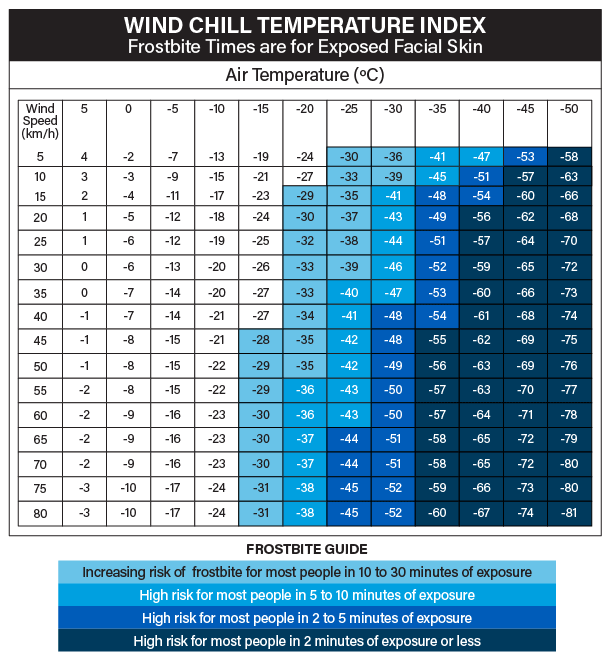
Cold Environments - Working in the Cold : OSH Answers
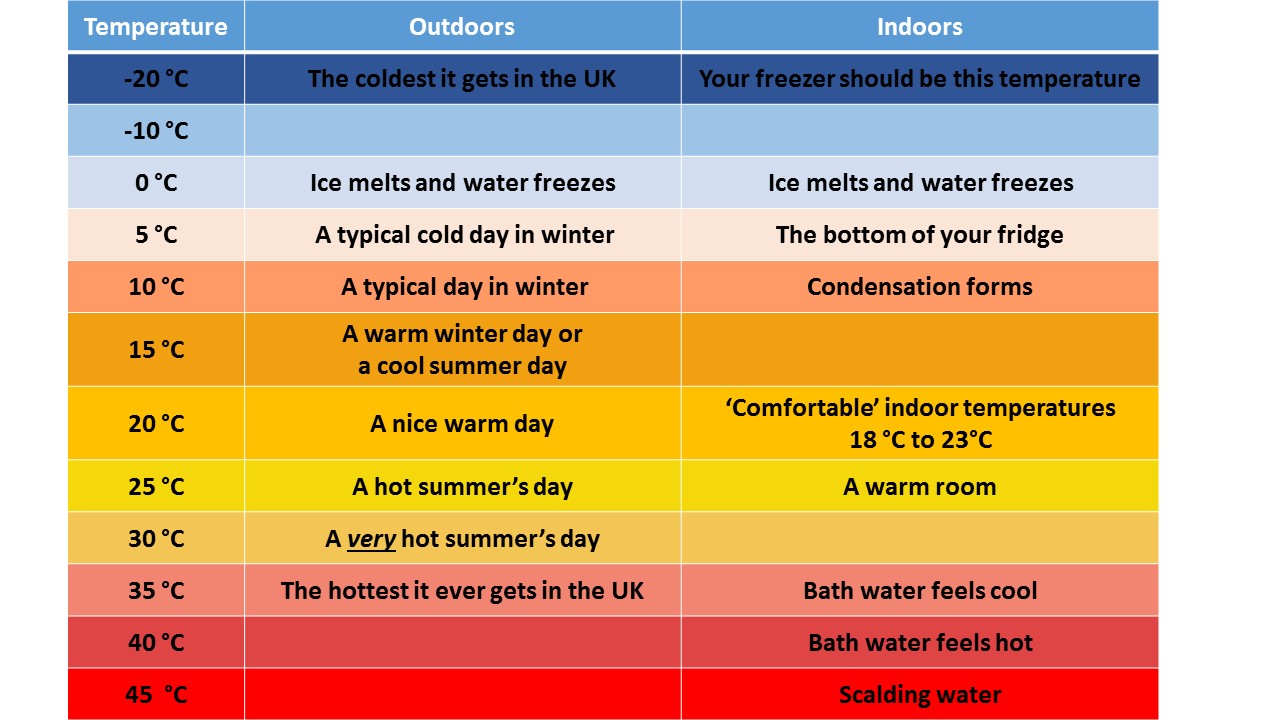
What's that in degrees Celsius? | Protons for Breakfast
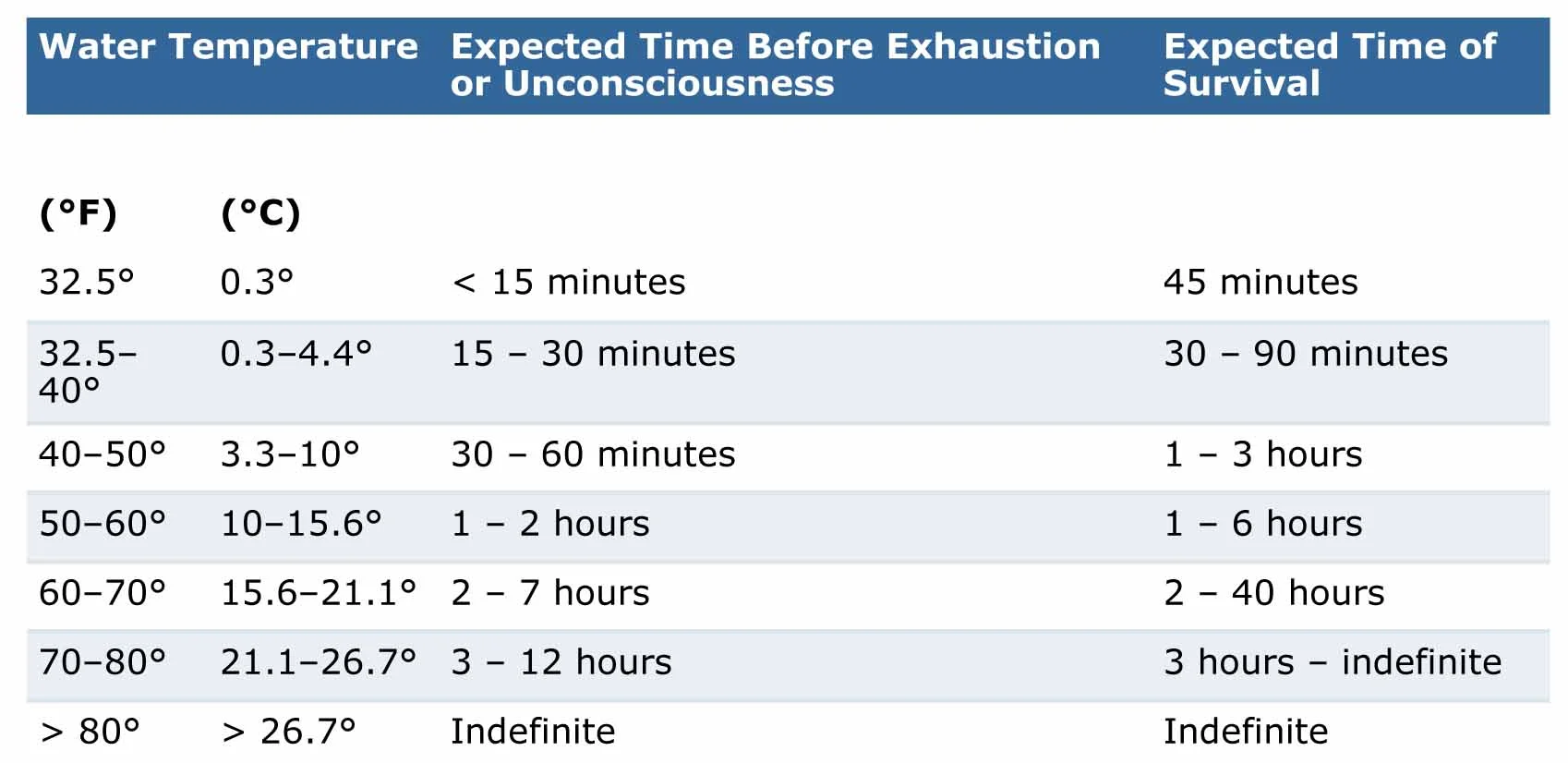
Safety in cold water — seas
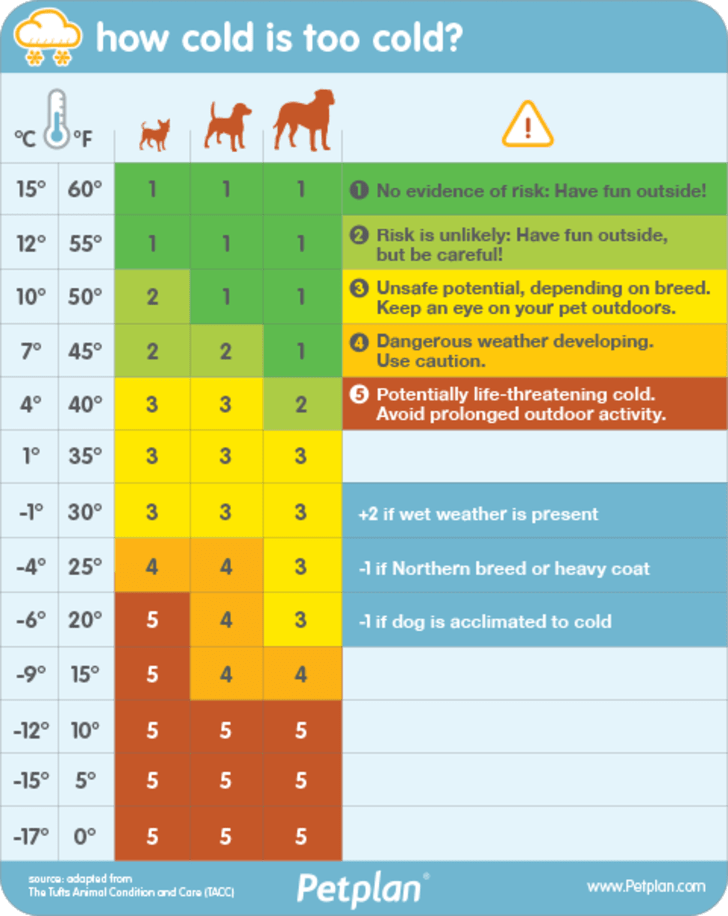
When It's Too Cold to Walk Your Dog Chart | Mental Floss

What Temperature Is Too Cold For My Dog? – The Pawsitive Co

Temperature | Science notebooks, Science lessons, Teaching science
AquaTopics: Temperature
Thermometer Icon Raster Celsius Fahrenheit Measuring Stock Illustration 338436167

Hot and Cold Temperature Unit Three What is Temperature? Temperature is a measurement of how hot or cold something is. We use a ______ to measure. - ppt download

Local Guides Connect - What temperature is considered as very cold in you... - Local Guides Connect
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/laundry-and-water-temperature-1900646-FINAL-5baa47d946e0fb0025b1cda9.png)
Choose the Correct Water Temperature for Laundry

Solar System Temperatures | NASA Solar System Exploration

Hot vs cold which water temperature is best for your skin by SameerK - issuu
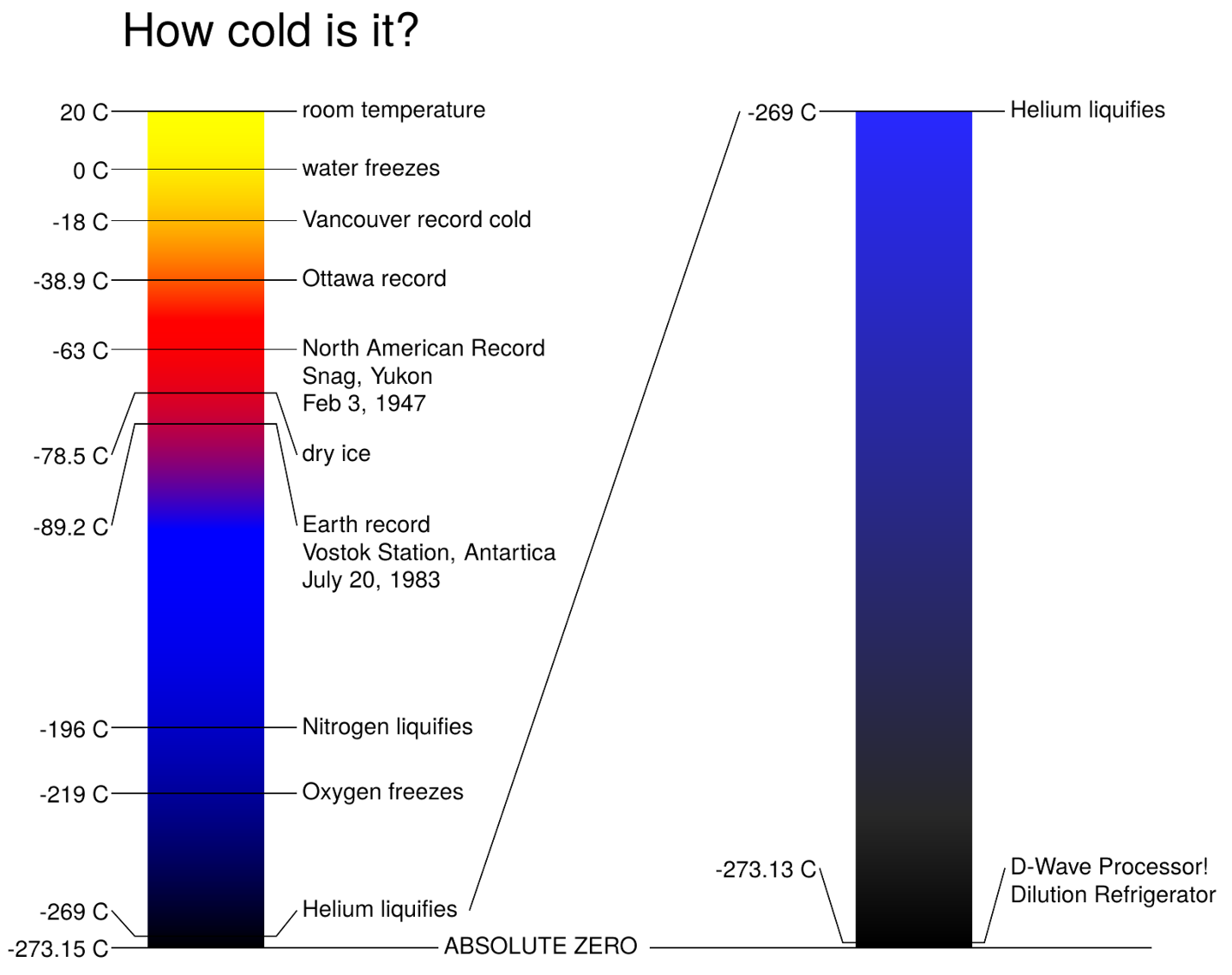
How Cold Is It? – D-Wave Systems

Question Video: Measuring Temperature in Celsius: Hot, Warm, and Cold | Nagwa
Lecture 11 - Temperature, conduction, convection, and latent heat
What temperature of water is too cold to swim in?" Redux | LoneSwimmer

Mpemba effect: Why hot water can freeze faster than cold

Results of the Cold Water Poll for Open Water Swimmers – Swim4Good

Cold Water Swimming Safety - NOWCA - Official website
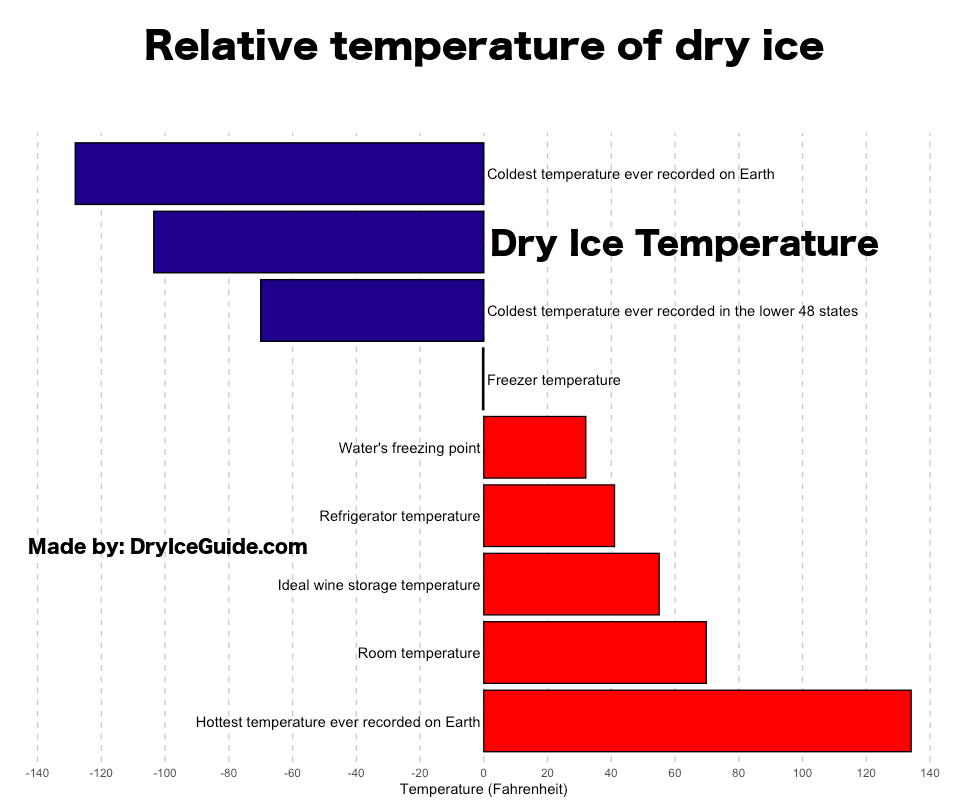
How Cold is Dry Ice? Comparing Dry Ice's Temperature - Dry Ice Guide

How Cold Should My Refrigerator & Freezer Be? - My Fearless Kitchen

Protecting Concrete in Cold Weather | FPrimeC Solutions Inc.

The Temperature in English - ESL Vocabulary
Cold Front: transition zone from warm air to cold air
How Long Can You Stay Outside In Cold Temperatures?

Temperature – Think Metric!

Staying warm in winter: What you need to know about cold weather clothing, hypothermia | WPDE
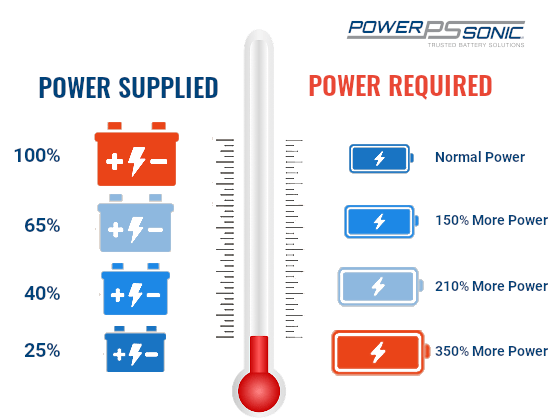
What Are Cold Cranking Amps & What does CCA Mean? - Power Sonic
The Painless Guide to Cold Showers - Primal Cold
Running In The Cold

How Cold Should My Refrigerator & Freezer Be? - My Fearless Kitchen
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/wash-with-the-right-water-temperature-2146348_FINAL-5bb51fb24cedfd0026d1752b.png)
The Best Water Washing Machine Temperature for Laundry

The Big Chill: Protection in Extremely Cold Weather
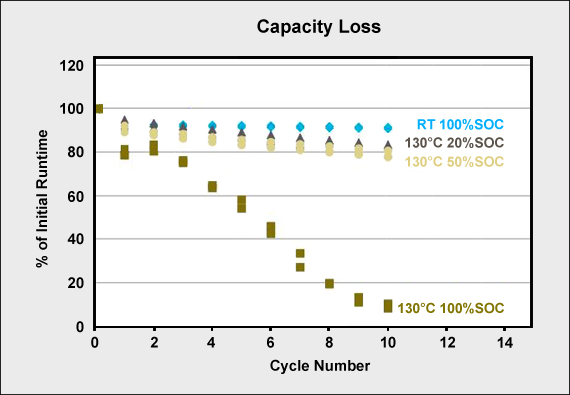
Charging Batteries at High and Low Temperatures – Battery University
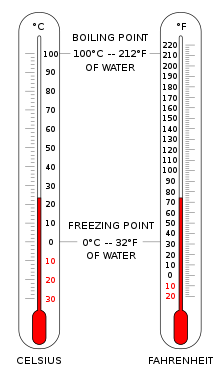
Temperature - Wikipedia

These Are The Hottest And Coldest Temperatures in The Universe, According to Conventional Physics
Posting Komentar untuk "what temperature is cold"